Point to Point Leased Lines (P2P) vs. Wavelength Circuits
Both Point to Point Leased Lines (P2P) and Wavelength Services are strong enterprise WAN solutions, but they vary in capacity, availability and pricing.

Nov 13, 2021
SHARE
Enterprises have many options when deploying Wide Area Network (WAN) services. The alternatives are plentiful and the pros, cons, differences, and similarities might not always be evident at face value.
Two options for your WAN that are deceivingly similar are Point-to-Point Leased Lines (P2P) and Wavelength Services. The two are similar in their network topology but differ in transport type, implementation, capacity, pricing, and availability. Your use case determines which fits your business best.
Let’s dive in to find out which is best for your enterprise.
What is a Point to Point Network Topology?
Network topology refers to both the physical and logical layout of a network. The former is the tangible items, like cabling and routers, while the latter is the software that controls information as it moves from place to place.
A point to point network topology consists of a direct link between two end points using a Layer 2 data connection, creating a closed network. With this form of network topology, each point in the network acts as both the sender and the recipient of the data.
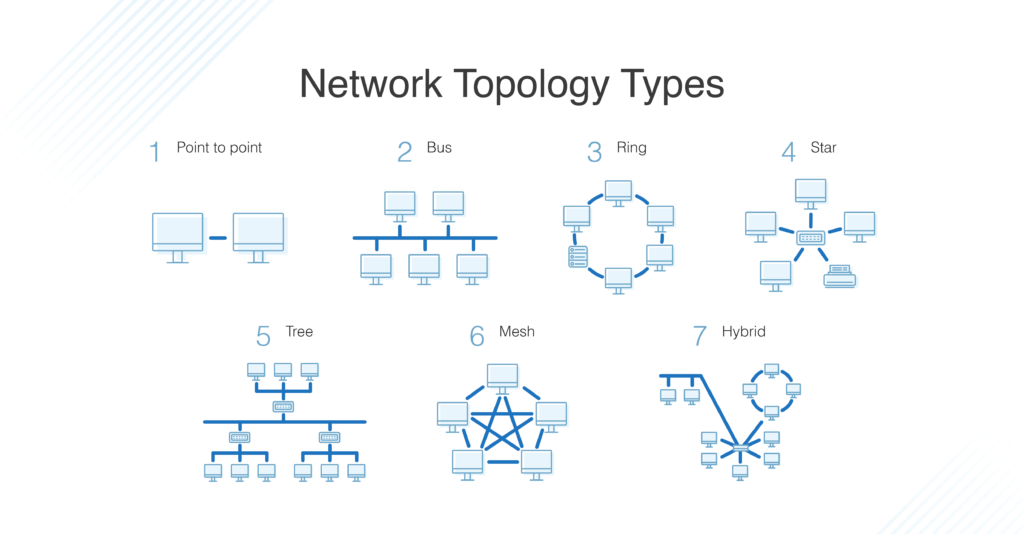
Source: DNSStuff
The image above shows different types of network topologies :)
What is a Point to Point Leased Line?
A Point to Point Leased Line WAN consists of direct, closed network connectivity transported over copper or fiber. Within a legacy P2P network, the equipment consists of a dedicated line leased from the local telecommunications service provider (T1/E1 and T3/E3) and two end nodes that support transmission speeds from 1G bps to 10G bps. Modern P2P networks are provisioned over fiber/ethernet and are available in speeds of up to 100 gbps.
P2P Leased Line data is transported by pulses of light over fiber - see diagram below.
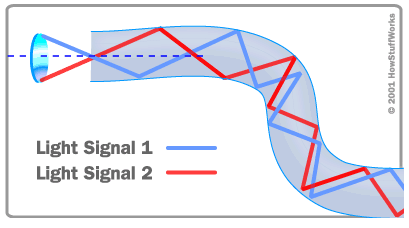
Source: How Stuff Works
P2P Lines have fixed, or static, routing across a carrier’s backbone and are unmanaged circuits, which means that the customer is responsible for more troubleshooting than they would be on an MPLS circuit. In some cases they can feature dynamic routing where a circuit heals itself in case of a network problem, but that’s not the norm.
Point to Point is a good fit for high performance applications. With the Internet, bandwidth is shared, so a business’ information is routed differently depending on traffic volumes and can be rerouted many times before reaching its destination. Consequently, performance varies, with packet loss, jitter, and latency running amok. P2P offers consistency because data always travels in the same way across a dedicated route. The only variable is how much information the client sends. Even then, corporations can ensure low latency for important applications by prioritizing traffic flows.
What are Wave Circuits?
Wave circuits also run on fiber optic networks but the mode of transport over the fiber differs, with Waves relying on Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) technology. Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is a transmission technique that uses multiple light wavelengths to send data over the same strand of fiber (see diagram below).
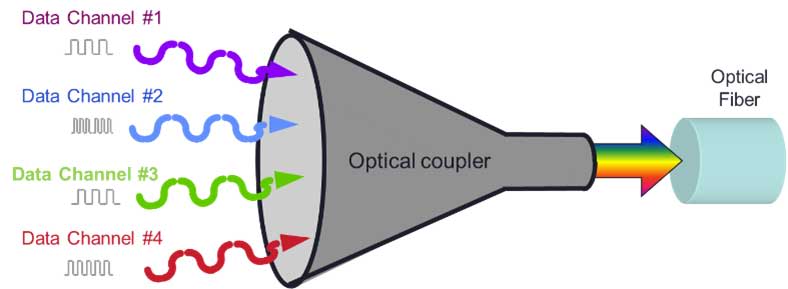
Source: Ciena
Cables are paired, so data streams in two directions at the same time, and any node on the network can send and receive information simultaneously. This option also supports both static and dynamic routing.
What to Consider When Comparing the Two?
Here’s everything you need to know when comparing P2P Leased Lines and Wavelength Services.
Bandwidth Needs
We’ll cut to the case: DWDM was designed for extremely data-intensive applications, so Waves are a much better fit for companies that have ultra-high bandwidth needs. The number of circuits provisioned varies based on the hardware that a carrier has deployed, but some vendors can offer as many as 192 “channels” over one cable. With each channel carrying up to 100G bps, the aggregate bandwidth capability is 19.2T bps over a single strand of fiber.
Pricing
We see P2P prices continuing to decrease as competition increases with wavelengths, dark fiber, and other types of connectivity growing in popularity. Wave is less expensive in general because it is a more efficient mode of transport as a carrier can provision multiple wave circuits over a single strand of fiber.
One fun tidbit on wave pricing - we’ve recently seen one provider quote $699 MRC for a 10 Gbps wave connection (this connection was data center to data center, but still a good data point to have in your back pocket).
From our pricing data (we’ve procured thousands of these things), the cost of P2P lines range from $950 to $2,000 for a 1G bps line while Wave pricing ranges from $500 to $1,500 for a 1G bps line.
For more on how these services are priced, check out our WAN Connectivity Pricing Guide.
Availability
Both P2P and Wave services are available in major metropolitan areas. However, given that P2P is more mature, it has a wider availability in domestic and international markets than Waves.
That said, many telcos are expanding their Wave capabilities (Zayo and Uniti are two recent examples).
Scalability
P2P and Wave were designed to carry large volumes of information between two endpoints. The benefit is they are easy to deploy and control, but a downside is they cannot easily add lines and scale up and out for companies with dispersed, remote work forces.
Other WAN options, like SD-WAN, offer enterprises more scalability.
Security
The network design of both of these options offers corporations a great deal of control over their enterprise network security; data on these connections does not travel on the public Internet, where it could be vulnerable to cyberattacks. So, these networks are often selected to protect sensitive information, such as financial and health care data.
Need Help Making the Right Network Purchasing Decision?
P2P and Wave circuits are popular network options because they provide a great deal of bandwidth, deliver consistent performance, and are well suited to applications where security is a high priority. If you want a simple, reliable solution, P2P is a good choice. If you have ultra-high bandwidth demands and are looking for more bang for your networking buck, Waves are a good fit.
If you’re still not sure, Lightyear can take in your specs and provide apples-to-apples quote options from multiple providers on your behalf for free. Simply fill out our 2 minute questionnaire if you’re interested in a quote.
Want to learn more about how Lightyear can help you?
Let us show you the product and discuss specifics on how it might be helpful.
Not ready to buy?
Stay up to date on our product, straight to your inbox every month.
